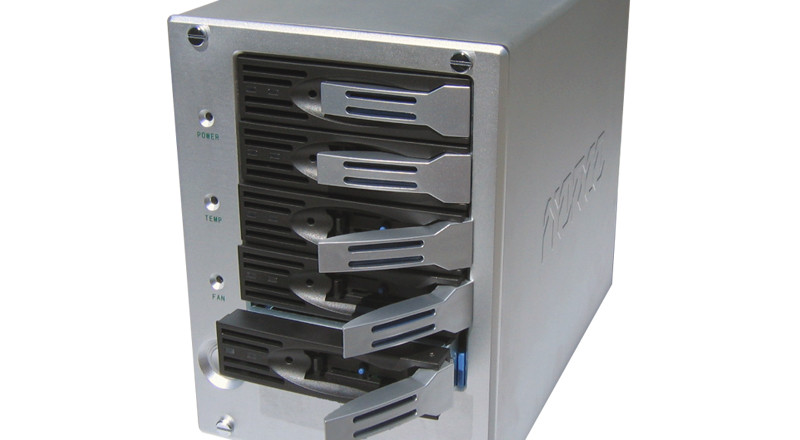
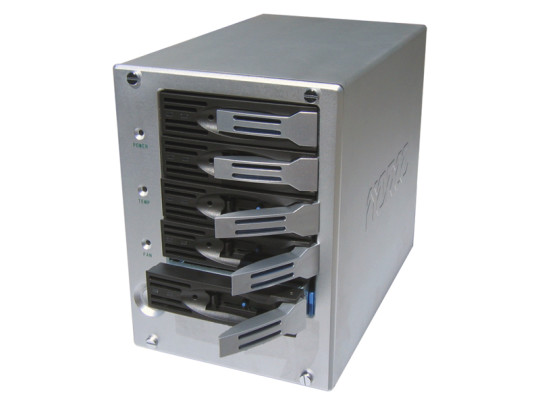
Find out what RAID is and whether your critical business systems need it. Learn all the basics to ensure your data stays secured regardless of your set-up.
RAID is short for “Redundant Array of Independent Disks”. The “I” in RAID can also be referred to as “Inexpensive”, which can also be true.
RAID stores your data across multiple hard disks for the benefit of:
Providing faster volume– Quicker to access data
Facilitates redundancy– Allowing seamless data access when a given number of disks fail.
In other words it helps prevent data loss when a hard drive fails by allowing the other hard drives to pick up the slack
One thing to bear in mind is that RAID data redundancy configurations are not immune to malware attacks, natural disasters and data beaches. As mentioned before, what it’s good for is preventing against hardware failure and maintaining uptime.
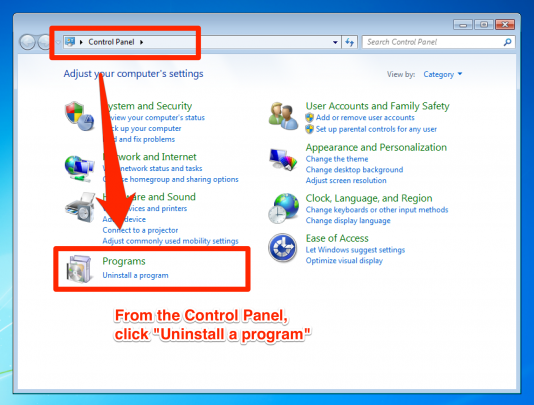
Popular RAID levels
RAID levels refer to how hard disks are configured to work alongside each other. There are three common RAID configurations that you’ll mostly hear about:
- RAID 0- offers the benefit of fast access to read and write data by having it distributed across the disks. The main disadvantage is that it offers no protection when a drive in this arrangement fails, as it’ll be the missing piece that jeopardises this arrangement leading to unreadable data.
- RAID 1– Mirrors the data in drives paired together. This offers better failover protections. In the case of one drive failing the data would still be available on the other disk whilst the failed drive is replaced. It also comes with the disadvantage of using up half of the disk space that is used to hold the mirrored data from the other disk. This means it’s a more costly solution.
- RAID 5– provides the best of both worlds, with data redundancy and faster access to it. It distributes data across all disks like with a RAID 0 setup and covers data with parity. In the case of failover, it’ll recover data like it does with RAID1. You’ll need to consider the minimum number of disks required for this setup, which is three, and uses one third of the disk capacity to hold the disk parity information.
- JBOD– Stands for “just a bunch of disks”. It’s not really considered to be a RAID however it is available alongside other RAIDs as a choice on most varieties of storage boxes. This only bunches a group of disks into one volume, where data will be filled until it becomes full and then moves onto the next available disk. With this, there’s isn’t any benefit of faster data access and redundancy. This is only good to use as a last resort.
What is RAID suitable for?
RAID is not really suitable for standard desktop computers, unless there’s a reason to store hundreds of gigabytes worth of critical data. Instead, it’s better suited on all servers and NAS (network attached storage) devices that share content and resources or that hold large amounts of data.
NAS devices simply act as additional storage that can be plugged into a network.
Since managing storage volumes on servers and NAS devices can seem like a headache to maintain, we suggest using an automated RAID management system such as SHR.
SHR by Synology, stands for Synology Hybrid RAID. It’s not even essential to know about all types of RAID setups as SHR takes care to quickly configure storage volume and deploy it according to your requirements. Unlike the classic RAID setups, SHR allows anyone to maximize their disk usage. There’s a lot more flexibility too, where you can scale up with additional disks within an already configured volume.
For more ways to secure your data and systems, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More