Solid state drives are non-mechanical storage devices which reduce load times and replace hard drives. Are solid state drives worth it for a small business?
What is an SSD?
Traditionally, the hard drive of a computer has always been a hard disk drive (HDD) made up of spinning disks covered in a magnetic coating to allow data to be read/written.
An SSD, however, has no moving parts and is powered by Flash memory. Essentially it’s a giant USB memory stick. And we all know how much quicker they are than fiddling round with disks!
SSDs, therefore, have become increasingly popular due to the speeds offered. In fact, sales of SSDs are currently doubling each year as HDD sales fall.
But what is it about SSDs that make them so appealing?
The Benefits of an SSD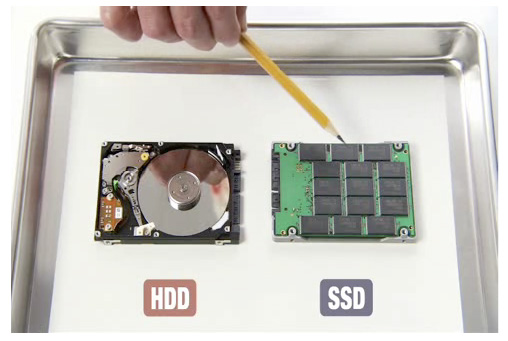
Increased Speed
We all get frustrated with the load up times for our computers and it’s even more irritating for business users who need to connect to numerous networks. However, by replacing an HDD with an SSD, users can find a 1 minute load time reduced to 15 seconds.
And it’s not just operating systems that receive this sprightly boost. Software such as Microsoft Office will also load in a fraction of the time.
Where SSDs really excel is their capacity to read and write data at speeds that are double that of an HDD. This results in a much quicker rate for creating and transferring files.
There are never enough hours in a business day, so anything which increases work time is a real bonus.
Better Data Integrity
A huge benefit of SSDs is that they’ll never crash and take all their data to silicon heaven. They simply stop writing data and preserve the current data load. Anyone who’s ever lost data to a hard drive crash will know that this is invaluable.
No Moving Parts
The fact that SSDs have no moving parts brings a number of benefits to your computer.
The main area of concern for a business is the process of wear and tear on an HDD due to the intense pressure the disk is put under by running at up to 7200rpm. An SSD, though, is never going to wear out and die.
No moving parts also make SSDs more energy efficient and help promote your business’ green image.
Is an SSD Worth the Extra Cost?
You’re probably getting quite excited over the prospect of SSDs, but they do have one drawback – the cost.
A 128gb SSD costs around $40 at the time of this writing, but a 160gb HDD can be as low as $15. This may not be a huge difference for a one off consumer, but if you’ve got a workforce of 50 computers then it begins to get pricey!
However, costs are dropping rapidly – as with all new technology – so SSDs are only going to become more affordable. You’re getting more bang for your buck with SSDs due to the increases in speed and reliability they offer.
For a small business, SSDs offer an exciting upgrade which will increase productivity and help your business reach the next level.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More