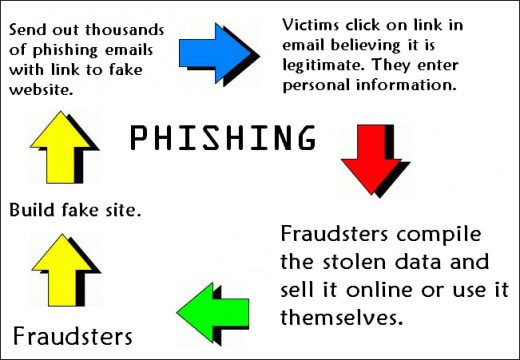
E-commerce means big business in the 21st century and it proves a highly attractive target to threat actors, as online sellers are now finding out.
Such is the size of the e-commerce industry – estimated to hit $4.11 trillion in 2023 – threat actors have many reasons for attacking online merchants. Taking control of a seller’s account will instantly provide hackers with a treasure chest of personal information about their customers e.g. payment methods, personal identifiers, and email addresses. It’s also common for threat actors to lace these compromised inventories and shops with malicious JavaScript code, this can then record credit card details during the checkout process.
Therefore, this latest attack, which uses the Vidar malware to advance its payload, is one that you need to be aware of.
How is Vidar Causing Havoc in the Digital Aisles?
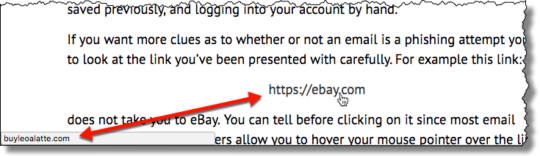
The attack launched against online sellers uses a combination of social engineering and phishing emails to deceive its targets. Threat actors are posing as disgruntled customers who claim to have had large amounts of money deducted from their bank without an order being processed. Using a bit.ly URL – which is typically used to shorten long URLs, but also hides the true destination of the link – the sender of the email advises the merchant to investigate a screenshot of their bank account. This, they claim, will show proof that funds have been taken.
Clicking this link will take the victim to a malicious website designed to look like a genuine Google Drive account. Here, the victim is encouraged to download a .PDF of the bank statement which the sender claims will demonstrate that an illegal transaction has taken place. However, rather than downloading a .PDF, the victim will instead download a file called bank_statement.scr. And this file contains the Vidar malware.
Vidar was first discovered in 2018 and its method of attack is well known. A classic data miner, Vidar will steal information such as passwords, browser cookies, text files, and also take screenshots of the infected PC. After uploading this data to a remote location, the threat actors can easily download this information and use it to exploit the victim further e.g. sell login credentials on the dark web or access other user accounts using the same information.
Taking Vidar Back to the Store
If you believe that your PC has been breached by Vidar, the good news is that most anti-virus tools will pick it up and eradicate it from your system. Nonetheless, it’s always better to not get infected in the first place. Therefore, make sure you follow these best practices to avoid falling victim to Vidar:
Pick up on suspicious language: phishing emails are full of telltale signs, but you need to know what you’re looking for. Firstly, look out for urgency, fear, and excitement-inducing words. Secondly, watch for requests to disclose personal information or click on suspicious links. And, finally, pay attention to poor grammar or spelling errors.
Only download from trusted sources: it’s advisable to only download files from sources you can verify are genuine. Downloading files from customers, even if they are genuine, should be avoided wherever possible. These files could, as the Vidar attack has shown, contain anything. In a scenario where you need verification, always turn to an IT professional.
Use anti-phishing tools: installing anti-phishing software is a good way to enhance your protection against phishing attacks. These tools can be implemented as either browser extensions or part of a security suite. Once they detect an attempt at phishing, they will block the content and present you with a warning in its place.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More