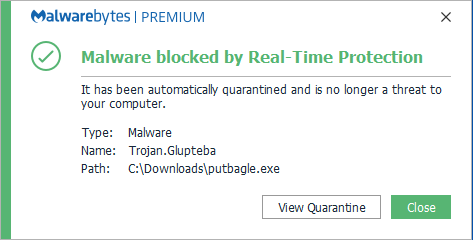
Despite experiencing a major obstacle a year ago, in the form of Google’s anti-malware efforts, the Glupteba malware is back.
First discovered in 2011, Glupteba is a veteran of the malware scene, although one which goes through periods of intense activity before disappearing for years at a time. A classic botnet, Glupteba has always focused on stealing data, but it has also made sure it has a backup plan in the form of targeting router exploits. Therefore, the news of its re-emergence is troubling for your IT infrastructure. And, given that Glupteba has been updated to be even stronger than ever before, you’re going to need to be on high alert.
Thankfully, we’re on hand to look at this malware and provide some critical advice on how to protect your organization.
Glupteba’s Latest Campaign
Following Google’s disruption of Glupteba’s botnet, which operated on the blockchain, Glupteba went quiet for several months. However, in June 2022 it was discovered that a new campaign had been launched, one which remains active as of this time of writing. Glupteba’s latest strategy targets Windows devices and has set its sights on harvesting data, using infected devices to mine cryptocurrency and setting up unauthorized proxies.
Glupteba is transmitted via traditional infection methods which include malicious installers (typically promoting themselves as free software installers) and through malvertising campaigns. As Glupteba is blockchain enabled, this gives it the ability to constantly change the command and control servers it uses. And, as it uses blockchain transaction data (which cannot be erased) to facilitate its attack, it’s very difficult to make a dent in the power of Glupteba’s botnet. These attacks often employ TOR services as well, a move which makes tracing the attacks next to impossible.
Staying Safe from Glupteba
One word in particular keeps being used when discussing Glupteba’s latest campaign: resilient. The source of its resilience comes from its design, one that uses deception and stealth to protect its operators and ensure it continues to spread. But this doesn’t mean you need to fall victim to Glupteba. If you make sure you follow good cybersecurity practices, you should be able to keep your IT infrastructure safe. All you have to do is:
- Understand the threat of malvertising: the internet is full of malicious adverts, but there are ways you can make your PC safer. The simplest way to do this is by installing an ad-blocker, these will block both irritating and malicious adverts, so it’s a win-win situation. Malvertising is also known to use exploits to spread its payload, so you need to make sure your browsers are fully patched and up to date.
- Monitor network activity: as Glupteba is a botnet, its operations are likely to lead to a spike in network traffic. And, if unauthorized proxies have been set up, this network activity is likely to go stratospheric. Therefore, you need to keep your network activity monitored to help you analyze any anomalies which may act as an early warning system.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More








