Due to their activities, hospitals need to be highly secure. However, a recent ransomware hack on UK hospitals has questioned just how secure they are.
Huge swathes of data are held by hospitals and the majority of it is highly personal and sensitive. Not only that, but hospitals rely on their IT systems to carry out highly important work such as maintaining operating equipment, retrieving patient information and even refrigerating blood samples.
Therefore, anything which even slightly impedes these operations can have a huge, disruptive impact. Unfortunately, for the UK’s hospitals (mostly run through the government NHS system), they have been hit hard by the WannaCry ransomware. Let’s take a look at how this major hack happened.
What’s WannaCry?
WannaCry is a form of ransomware that exploits a vulnerability contained within the Server Message Block (SMB) which is a network protocol to help facilitiate access to shared files and printers etc. It’s not yet been revealed exactly how WannaCry has managed to infect the UK’s hospital systems, but it’s rumoured to be through the usual infection methods of Microsoft Office attachments or suspicious links.
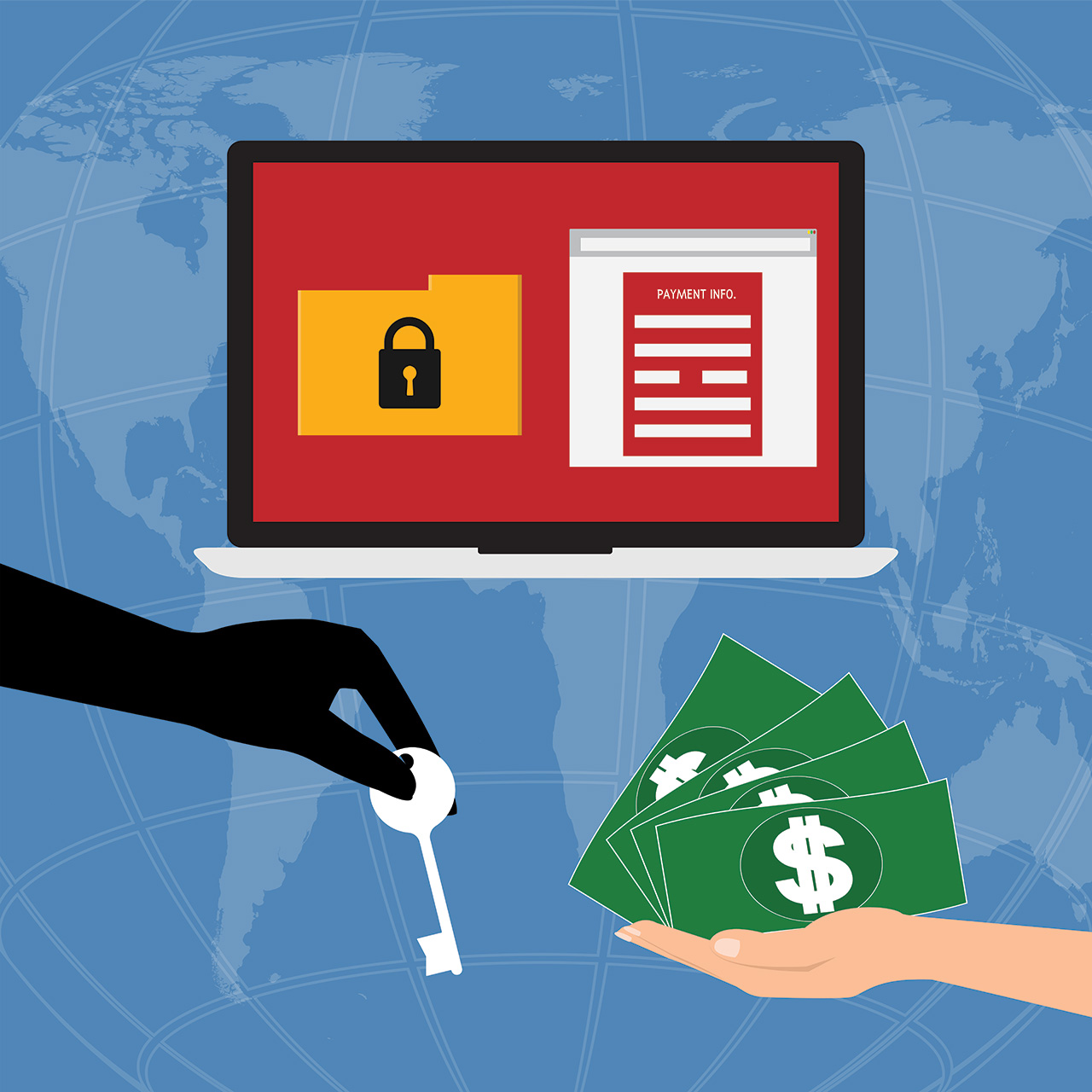
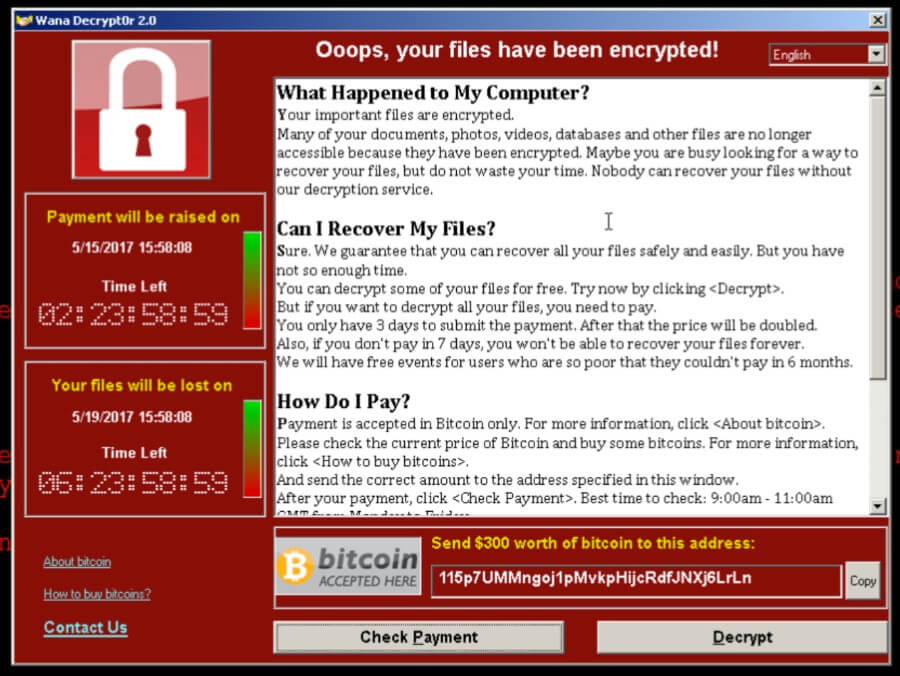
Once WannaCry is executed in the SMB it begins to encrypt almost all the files on that PC with an extension of “.WRCY” and then displays a ransom window which demands payment of $300 worth of bitcoins to decrypt the compromised files. A ransom note is also placed on the users system in the form of a text document to detail the ransom demands once more.
What’s surprising about this attack is that the SMB vulnerability was actually patched by Microsoft almost two months previously in March. Those users and networks who implemented this patch will have survived the WannaCry attack, but countless others failed to install the patch. It’s suspected that many of the UK hospitals attacked were unable to install this patch due to the number of legacy systems involved.
And it’s not just the UK’s hospitals which felt the wrath of WannaCry. Car giant Nissan found that their UK manufacturing plant was also attacked and this led to production of their cars being halted. However, it isn’t just the UK which was targeted as reports show that over 40,000 similar attacks have now been registered in over 70 countries.
Avoid the Ransom Demands
It may seem difficult to combat such a huge, global cyber-attack which is capable of bringing government organizations to their knees, but prevention can make a real difference in these situations.
The most important lesson to learn from WannaCry is that updates issued by software manufacturers must never be ignored. Sure, it may require a quick reboot, but surely a few minutes inconvenience is preferable to having all your files compromised and in the hands of an anonymous attacker?
It’s also vital that you have up to date antivirus software and network protection as, in the case of WannaCry, these can identify the ransomware before it has a chance to take hold of your computer. Again, these can be inconvenient due to the cost, but the long term benefits to your organization can be immense.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More