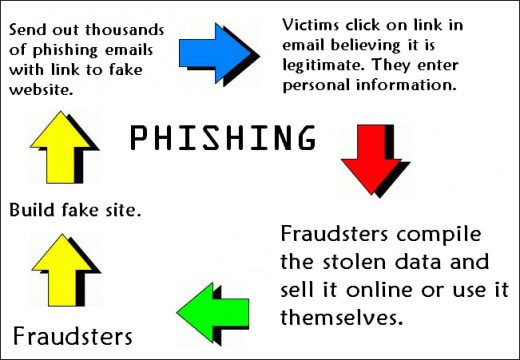
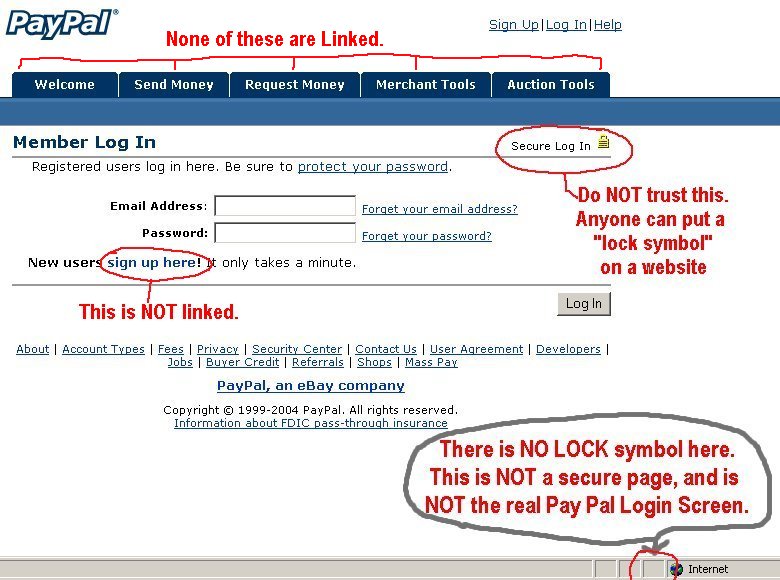
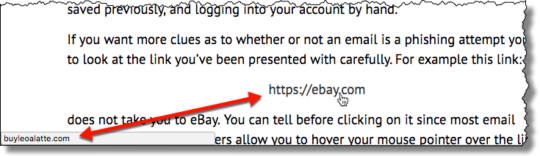
Thanks to the power of social engineering, phishing remains a powerful method of hacking organizations. Reducing this risk, therefore, is crucial.
Phishing has been active since the early days of the internet and, unfortunately, it doesn’t appear to be going anywhere soon. Thankfully, you don’t have to fall victim to these deceptive attacks as there is plenty that any organization can do to protect its data. And, don’t worry, it doesn’t involve investing millions in state of the art technology. All it takes is a little bit of common sense and an understanding of how phishing attacks work.
To get you started we’re going to show you how to reduce the risk of phishing attacks.
Antivirus Software is Key
One of the best ways to reduce phishing emails is by working with antivirus software. Capable of scanning attachments and analyzing links contained within emails, a good antivirus software can easily target the two main ways that phishing attacks unleash their payload. However, as with all software, it’s important that you update it regularly and install updates immediately. Phishing attacks can spread round the world very quickly, so you need to stay one step ahead of them.
Keep Up to Date with Phishing Attacks
Hackers are constantly developing their techniques and tweaking their methods, so it’s vital that you keep an eye on what’s happening in the world of phishing. New attack methods can be launched very quickly and be in your inbox within a day, so make sure that you’re regularly monitoring IT news sources to prepare yourself for any incoming threats.
Educate Your Employees
The main targets of any phishing attack against your organization will be your employees, so they have to be educated in order to prevent any data breaches. The basics of phishing are relatively simple, so the training doesn’t need to be too in-depth. All you have to do is ensure that these basics are hammered home so that employees know how to spot a phishing email and how to deal with it.
Practice Phishing Attacks
A popular method for reducing the risk of phishing attacks is by running regular exercises to test your employees. For example, fake phishing emails can be randomly emailed to your employees that test whether they are susceptible to phishing scams or not. Usually, these emails will contain a fake link that urges them to complete something on behalf of the company – such as IT training – but the actual URL contained will be a ‘malicious’ one. Those employees that fail to spot the ‘malicious’ link can then be asked to take a refresher training course.
Combine All Your Preventative Methods
The key to reducing the risk of phishing attacks is by combining all of the above into one multi-faceted security approach. An amazing antivirus software solution, for example, isn’t effective enough on its own. Instead, you need a firm knowledge of the phishing landscape, amazing employee training and regular tests to guarantee that you can tackle phishing on all fronts.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More