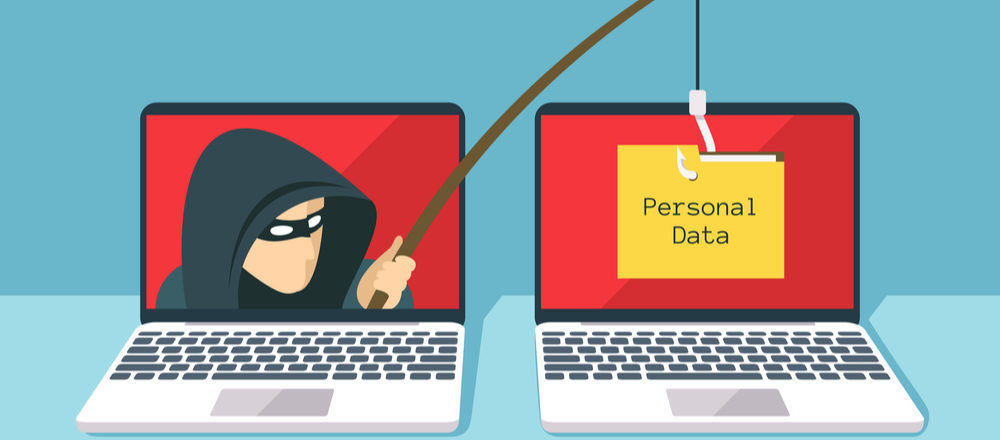
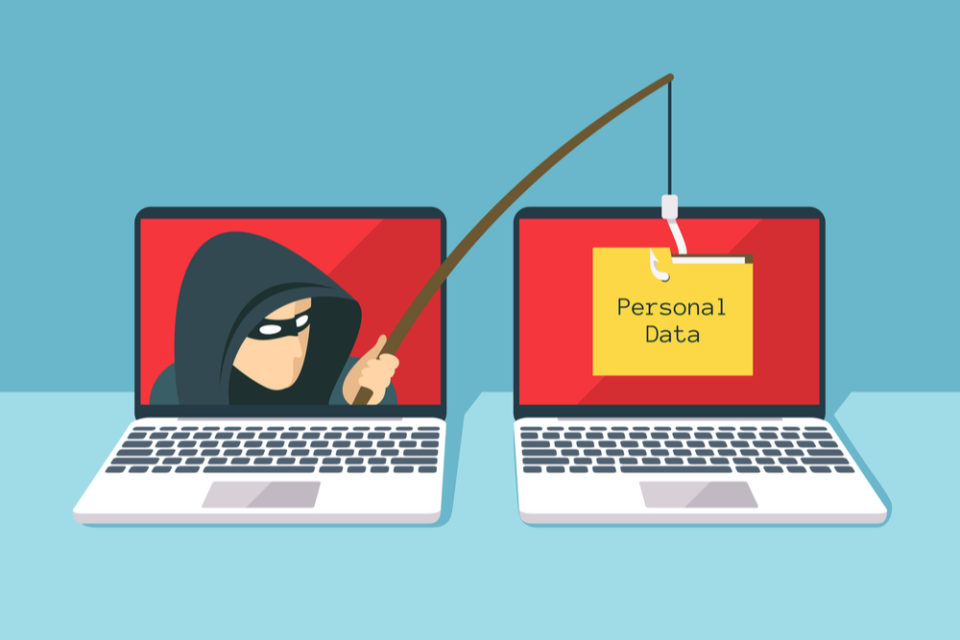
Cyber-crime remains a major threat to any organization that works with IT, but the basics of IT security are often the best way to counter this threat.
Cyber-crime remains a major threat to any organization that works with IT, but the basics of IT security are often the best way to counter this threat.
It’s difficult to avoid the fact that cyber-attacks are reaching record levels. IT systems are less secure than ever and need protecting. And that’s where your organization needs to take up the baton. Protecting these systems may sound like a monumental task, but it’s a lot easier than you think. Key to success is following the basics of IT security. The simplicity behind these processes is remarkable and can make a significant difference.
It’s crucial that you know what these are, so let’s take a look at the very basics of good IT security. 
Understanding the Basics
The complexity of IT systems often means they’re difficult to work with. And from this complexity comes flaws in security. The good thing is that IT security doesn’t have to be difficult. The best way you can help protect your IT system is by following these basics:
- Multi-factor Authentication: A password is a fantastic way to protect your IT systems, but why should you stop there? Multi-factor authentication looks to strengthen the login process by introducing extra steps. An example of this could involve texting unique codes to mobile devices to complete the login process. This method of IT security allows you to reduce the risk of employees’ login credentials being compromised.
- IT Inductions: You should never assume that new employees have a solid understanding of IT security. And that’s why your staff should always have to complete an IT induction. Not only will this familiarize them with the technology you use, but it allows you to run through the basics of cyber threats. This knowledge can make a real difference in strengthening your defenses.
- Disable USB Ports: The level of damage that USB devices can cause is shocking and unbelievable. Your employees are unlikely to be aware of this threat. To them, a USB port is simply a handy device for charging their mobile device. The truth is much different. This threat can be extinguished by disabling the USB ports. This can be achieved by adjusting the USB settings for your employees.
- Use Antivirus Software: It may feel like a simplistic step in IT security but antivirus software remains essential. Good antivirus software can recognize malware within milliseconds and flag it. A manual scan will never be able to match this. And your employees wouldn’t know what they were looking for. The vast databases in use and the speed in which they operate ensures that antivirus software is a must have in business.
- Assign Privileges Accordingly: Different employees will need different network privileges. These variations arise from the different tasks they perform within your IT system. Certain departments, for example, will need access to one drive whilst another department will not. Understanding these differences is critical. Once the necessary privileges have been identified then you can minimize the risk of cyber-attacks spreading through the entire system.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More