You may think that political parties understand the need for good security, but back in 2016 the DNC suffered a major hack due to phishing emails.
Thanks to a sustained attack, Russian hackers were able to infiltrate email accounts of those involved within Hilary Clinton’s campaign to become president of the United States. And, as you know, the rest is history. However, not many people are aware of exactly how the DNC got hacked so extensively that highly sensitive information was obtained and then leaked to the public.
Although not every single detail has been revealed, we know enough that the hack was, in relative terms, a fairly simple execution. Naturally, you’re unlikely to be targeted by the same people who are involved in political attacks, but their methods are likely to be similar. Therefore, we’re going to take a look at how the DNC was hacked by phishing emails, so you can understand how to avoid it.
Phishing for DNC Secrets
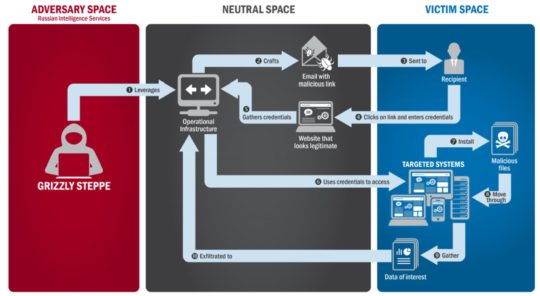
The hack began on March 10th, 2016 and involved a batch of heavily disguised emails, which appeared to be sent by Google, being sent to key members of Hilary Clinton’s campaign team. These emails purported to be advising the recipients that their passwords needed changing in order to strengthen their security. However, the links contained within these emails sent users to a malicious website where strengthening security was the last thing on their mind. With these email accounts compromised, the hackers were then able to access private contact lists held within them.
Within a day, the hackers had access to confidential email addresses for key targets within the DNC campaign. And, almost immediately, the hackers began to send phishing emails to these email addresses in order to work their way higher up the chain of command. Despite the presence of two-factor authentication, the hackers’ persistence paid off as they eventually managed to breach the defenses of John Podesta, chairman of the DNC’s campaign. This email account, alone, provided access to 50,000 confidential emails.
This assault is believed to have been organized and orchestrated by the Russian cyber-espionage organization known as Fancy Bear. Despite accessing such a huge amount of emails from Podestra, Fancy Bear intensified their hacking campaign and this led to security experts becoming suspicious of methods being employed to dupe Google’s spam filter into accepting malicious emails into the inboxes of DNC targets. The clean-up operation, however, was too late and Podestra’s breached emails were soon published on Wikileaks.
Be Clever, Don’t Get Phished
The 2016 attack on the DNC is probably the most famous, and damaging, phishing attack in cyber-history. Simply due to a few members of staff clicking malicious links, an entire election campaign was brought to its knees. Reinforcing good email security, therefore, remains a crucial practice for any organization in modern business. Even with millions of dollars of security in place, the DNC fell victim to a simple phishing scam and, next time, it could easily be your organization.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More