The sheer range of PCs available makes choosing a new one very difficult. But in business there’s no time to waste, so you need to know what to look for.
Take a look at the spec sheets for two different PCs in the same price range and you’ll notice something: no two specs are the same. One could have an Intel processor whereas the other might have an AMD processor. Likewise, one PC may have an Intel processor with a speed of 2.9GHz while the other PCs Intel processor is measured at 4.1GHz. So, as you can see, choosing a new PC can be a baffling process. And we’ve only scraped the surface of the differences between processors.
Purchasing a new PC needs to be an informed decision, but it doesn’t need to take forever. And our guide on three things to look at when buying a new PC should give you a head start.
Knowing What to Look For
You don’t need to be an IT technician to understand what you need in a PC. The information is freely available and easily understandable. But, to point you in the right direction, we recommend focusing on the following three things:
- RAM: Random Access Memory, better known as RAM, is a crucial element in the way in which a PC performs. The simplest way to describe RAM is as the working memory of the PC. It’s a temporary space where a PC can store and access data that it is currently using. Accordingly, the more applications you have to run at the same time, the more RAM you need. Choosing a PC, therefore, will rely heavily on the number of data heavy programs you use on a regular basis. If in doubt, overestimate the amount of RAM required.
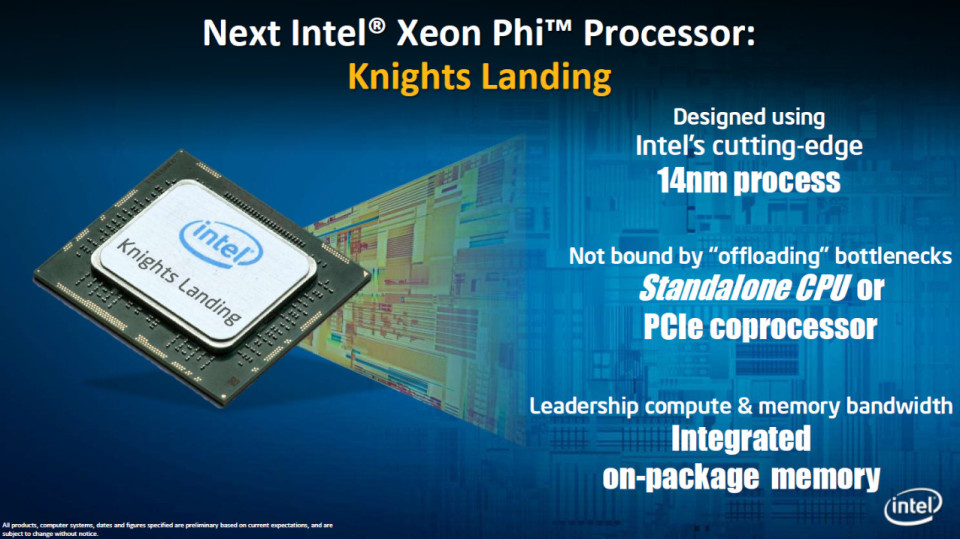
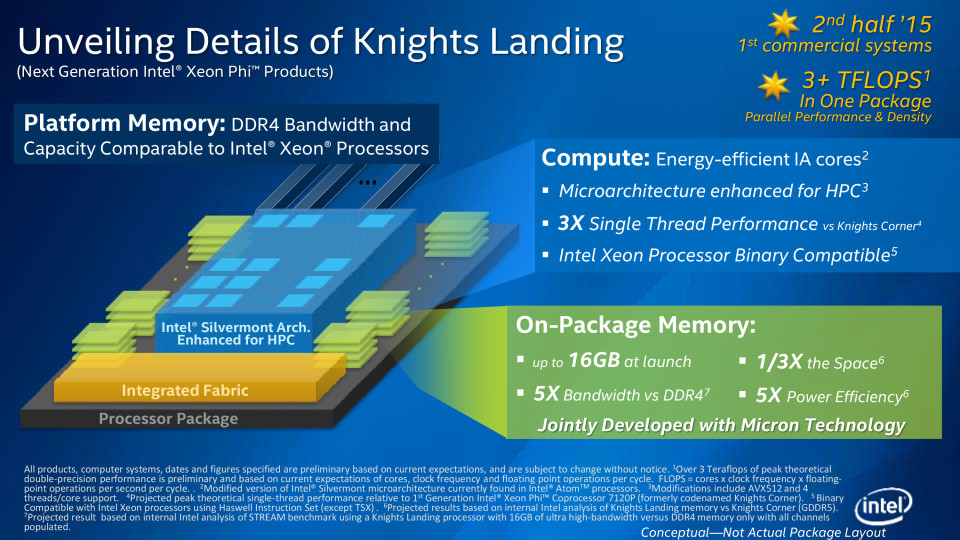
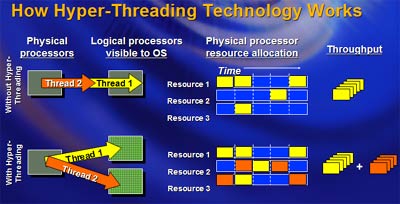
- Processor: The performance of your PC is dependent on the processor located at its core. This doesn’t necessarily mean that faster is better. A high speed processor (4GHz +) is only necessary if the PC is to be used CPU intensive tasks such as 3D rendering and video encoding. If, however, the PC is to be used for simpler tasks such as word processing and database work then it pays to settle for a lower speed processor. The minimum that any business should be investing in is a four-core processor, so don’t go any lower.
- Graphics Card: There are two main forms of graphics card available: integrated and dedicated. And the one that is right for you will depend on what you will be using the PC for. An integrated graphics card, which is built into the main motherboard, is most suitable for basic, everyday usage which doesn’t require powerful graphics. If, however, your work involves video editing and coding/playing video games then you will need a dedicated video board which is installed as a separate component.
Final Thoughts
You will, of course, need to consider countless other aspects when purchasing a PC, but these three starting points will save you a lot of time. It really is a buyer’s market when it comes to choosing a new PC thanks to the level of availability on offer. And, if you purchase the right PC, it will deliver the performance your business needs on a daily basis.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More