Hackers thrive upon deception and the result of this endeavor is social engineering. It’s a powerful tactic and one you need to protect yourself from.
Social engineering has been used to deploy attacks such as the Coronavirus malware and the recent attack on high profile Twitter accounts. The method is intriguing due to its sophistication and its human element. Rather than relying on complex coding techniques to outwit computer systems, social engineering takes advantage of human naivety. More importantly, however, is the sheer destruction that it can cause.
The world is a perilous place at the best times, but now more than ever we need to make sure we protect ourselves and our businesses. One of the best ways to get started is by reinforcing the barricades against social engineering.
What is Social Engineering?
Manipulation is, in a word, exactly what social engineering is. But you’re going to need a little more information than that, so let’s take a closer look.
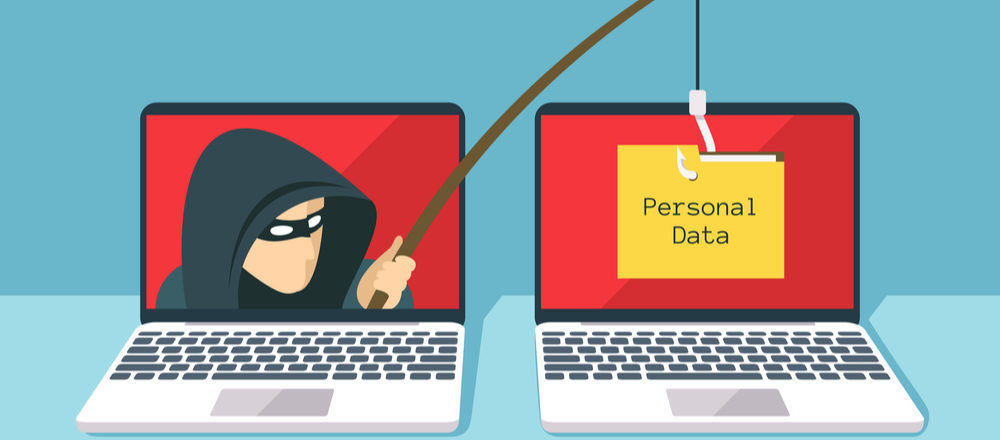
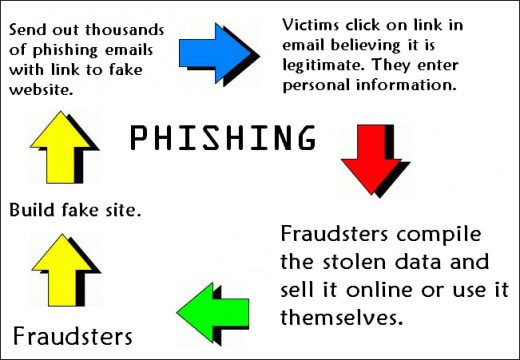
Social engineering is a process in which one party seeks to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information. When it comes to the world of IT this sensitive data tends to relate to login credentials, but can also involve transferring sensitive documents such as employee records. These attacks are commonly executed through the use of phishing emails, but this is not the only technique. It’s possible for hackers to carry out social engineering attacks over the telephone and even face to face.
The Best Ways to Protect Yourself
Protecting yourself against social engineering takes a concerted effort. You can’t rely on software alone to protect you. Luckily, you can strengthen your personal defenses by practicing the following:
• Take Your Time: Social engineering relies on a lack of caution on the victim’s part. Therefore, it’s crucial that you always take your time when it comes to any form of communication. A social engineer will do their best to force you into making a quick decision e.g. clicking a link or disclosing your password. To counter this, evaluate all requests and press for answers if you feel even slightly suspicious.
• Use Email Filters: There have been great advances made in email filters over the course of the last 20 years. Where these junk filters once had relatively little use they are now highly intelligent. Enabling your email filters will enhance your security and prevent the majority of phishing emails making their way into your inbox. This reduces your risk and stops you from engaging with a social engineer.
• Too Good to Be True: As with all areas of life, if something sounds too good to be true then it makes sense to be suspicious. After all, it’s unlikely that a representative for an African prince wants to deposit millions of dollars into your bank account. And, if they did, why would they require your social security number? And your workplace login credentials? As a rule of thumb, if it sounds like a scam then it probably is and should be deleted.
• Is the Source Genuine: If an email says that it’s from your bank then this doesn’t mean it’s from your bank. Likewise, a phone call from your HR team isn’t necessarily genuine. Hackers specialize in trickery and deception, so they won’t shy away from such blatant and direct approaches. Always check every request for details such genuine URL details (by hovering over a link) and only transmitting sensitive data to internal email addresses.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More