In response to a decline in PC sales, Intel has unveiled their new processor – 6th gen Core vPro – which promises to transform business computing.
PC sales fell by 10.6% during Q4 2015, so growth in the market appears to be slowing down. Naturally, this is the last thing that PC manufacturers want to hear, so will Intel’s new chip give the market a shot in the arm?
It’s an intriguing question and, to fully understand it, we need to take a look at why the market has slowed down and what Intel’s new processor can bring to the table.
Decrease in Sales
The number of new PCs sold in 2015 fell below 300 million and, whilst this sounds a huge amount, it’s actually the lowest number of yearly sales since 2008. Consumers, then, appear to be holding off on that glittering upgrade, but why is this?
Well, back in the early 00s, you could expect the cost of PC processors to fall every 18 months whilst the number of transistors would double – this was known as Moore’s law. The result was a cheaper, but more powerful processor. And businesses, keen to stay at the cutting edge of technology, were happy to upgrade to maintain an advantage over competitors.
However, as we’ll discover, Moore’s law has not remained constant and the speed increases are not what they once were.
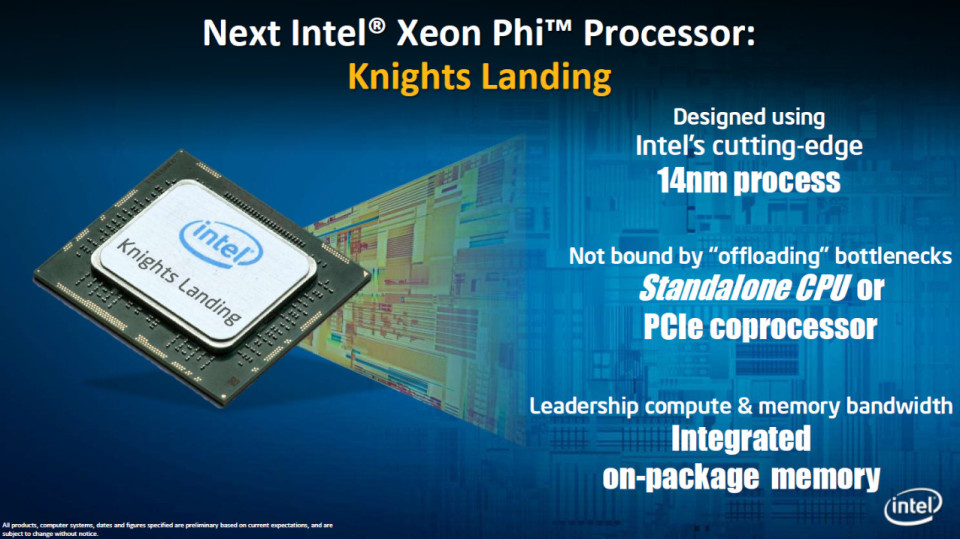
Introducing the 6th Gen Core vPro
The question on most consumers’ lips – as ever – is “will this processor speed up our business operations?” and the answer is a resounding YES! However, although, the increase in speed is estimated to be around 2.5x faster, this is only when compared to a 2011 PC.
The increase in speed is relatively small compared to previous advancements in speed. Couple that with an increase in the cost of transistors and you can see why progress has slowed.
Speed has increased, though, and Intel’s new chip has plenty more to tempt businesses into parting with their cash.
Intel has also improved the efficiency of their conference connectivity software Intel Unite to provide smoother connections between the myriad of different adapters and connections. This will sound like an absolute dream for anyone who’s ever tried to set up video conferencing!
Also at the forefront of Intel’s sale pitch is their strong focus on security. We live in a world where the potential for cyber-attacks seems to increase by the day, so Intel is moving into hardware based security. Utilizing multi factor authentication, Intel Authenticate will aim to reduce current data security threats by around 25%.
And this will involve much more sophisticated methods than SMS authentication or old fashioned passwords. Intel is moving into the 21st century with fingerprint scanning and smartphone/PC proximity checks.
Will PC Sales Increase?
Intel is certainly putting all it’s got into making sure the 6th gen Core vPro succeeds and I think they’ve got a good chance of achieving this. The increase in speed – although smaller than is historically expected – will be a real boon for businesses as will the enhanced security in an unsecure landscape.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More