Learn how USB thumb drives can potentially destroy laptops / pcs. We’ll explain how this works and what measures can be taken to protect your computers.
If you happen to find an unknown flash drive in any place that you aren’t familiar with, we strongly advise not to plug it into a computer, especially one that is used for work. It makes sense when there’s a high element of risk involved. Not only does the possibility of being infected by a virus exist, but as of late, a new type of attack has been created which can physically damage your systems. We have recently learned of dangerous USB thumb drives that are capable of frying a computer or laptop.
How does it work?
Think of a computer’s ports as physical access points for an attack.
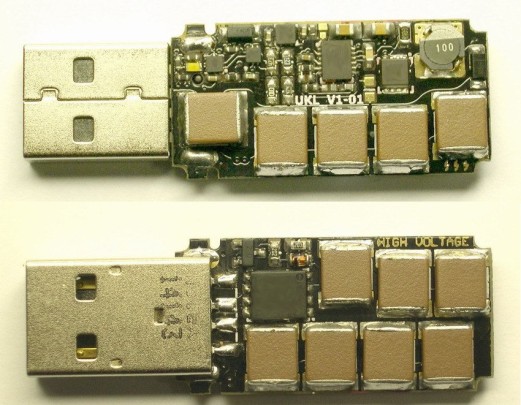
- An attacker would modify or build a USB thumb drive by using an inverting DC-DC converter to draw power off the USB port.
- The power drawn from the USB port is then used to create a -110VDC charge on a capacitor bank.
- Once the caps have charged up, this triggers the converter to shut down.
- This forces a transistor to propel the voltage from the capacitor over to the port’s data pins.
- This pattern repeats every time the caps recharge, discharging its high voltage through the port.
- As long as there’s a bus voltage and high current present, the attack will run its course and overrun the small TVS diodes present on bus lines of the computer or laptop.
- Inevitably this will lead to a computer’s components, including possibly the CPU, to fry.
- With fried components, a laptop or computer will be “dead”.
In typical circumstances a USB thumb drive is design to be protected, and a computer is normally able to dissipate manageable amounts of power, which wouldn’t cause this type of damage.
An example of an attack
A thief had stolen a USB flash drive off a commuter on the subway. When the thief inserted the flash drive into his computer USB port, the least he’d expected was to see some data. Instead, his computer died as its internal components have been fried. Although one may think that it was good for the thief to get their just desserts, it addresses a more serious problem- trusting unknown peripherals such as flash drives.
Precautionary measures
Now that we have a good overview of how a USB thumb drive can be engineered to take out a computer, let’s discuss how to prevent such an occurrence.
- Don’t allow strangers to connect a USB thumb drive in to a mission critical computer or laptop.
- Don’t plug in USB thumb drives found in public.
- Do only use thumb drives purchased from reliable retailers or officially provided by an IT administrator.
- Avoid sharing thumb drives, especially if they leave the premises and return to be used on computers.
- Aim for individuals to carry their own thumb drives which can safely be used within an office environment.
- Always question any thumb drives which may be presented to your business by an unknown third party. Even if it lands at your office’s reception desk, have an IT admin check it out first.
- Have a thumb and flash drive policy in place to cover all of the above as part of your IT security policy.
For more ways to safeguard your computers and IT infrastructure, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More