The terminology used to describe various hacks and security threats usually includes the terms malware, ransomware and virus, but what exactly are these?
It can get a little confusing when discussing the various security concerns that are floating around and this confusion can lead to a lapse in security. After all, if you’re reading about malware, but don’t know exactly what it is you’re reading about, then you’re going to be unable to act against it. And that’s why we’re going to take the time today to explore each particular category in a little more detail.
What is Malware?
Malware is very much an all-encompassing term for any form of malicious software, so this can include ransomware and viruses. However, we’re going to cover those two categories in depth later, so for now we’ll look at some other types of malware:
- Spyware: Installed on a user’s PC without their knowledge, spyware is software that can be used to track user activity and then transmit this to a remote server e.g. keystrokes can be recorded to determine and steal login details.
- Bots: Capable of bringing entire networks to a halt, bots are a particularly troubling form of malware that can easily harness the power of an infected PC to carry out spam email campaigns or DDoS attacks.
- Rootkits: Highly conspicuous and deceptive, rootkits allow hackers to take control of infected PCs from a remote location. Usually installed at a root level, hence the name, rootkits provide privileged access to the victim’s PC.
What is a Virus?
Much like the common cold, a computer virus is an infection which can spread quickly and effectively. Exposure to a computer virus usually occurs when the PC encounters an infected website or file. Following this exposure, the virus is downloaded to the PC and executed. And this can generate the following results:
- The PC startup process can become corrupted and leave users unable to log on to their workstation.
- Performance levels can suddenly drop as your PCs processing power is handed over to the virus’ tasks.
- PCs can find themselves spammed by numerous popup adverts which, if they’re particularly virulent, can soon crash the computer or slow it down significantly.
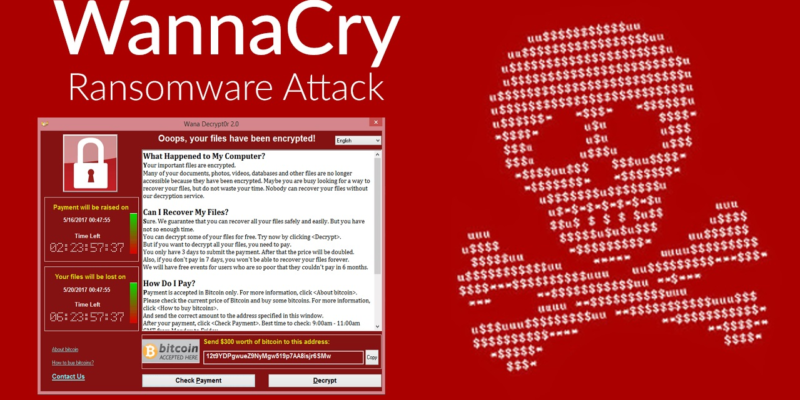
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware has grabbed countless headlines over the last few years and it remains a pressing concern for any business. Most commonly spread through phishing emails, ransomware’s main objective is to extort a ransom in exchange for the release of files it has encrypted.
Once the ransom has been paid then the hackers should, in theory, supply a key to decrypt the files. However, it’s becoming increasingly common for hackers to take the ransom, which is usually demanded in untraceable cryptocurrency, and leave the compromised files encrypted.
Final Thoughts
Whether you find your PCs affected by malware, a virus or ransomware, it’s clear that they spell danger for your organization. It may sound a little clichéd, but when it comes to malicious software then prevention is the best cure. And one of the best ways to prevent your PCs from falling foul of infection is by educating yourself on exactly what you’re up against.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More