Passwords are one of the most common security measures, but they’re still considered a risk. And 26 million stolen passwords have just been found.
We all use passwords on a regular basis throughout our working day. Logging on to remote servers and online platforms all require a set of login credentials. And, on the whole, they provide an adequate level of security. But security which is considered only adequate will always remain a tempting prospect to hackers. Login credentials will typically consist of only two pieces of information: username and password. Naturally, with only two data values required – which can be entered from any keyboard – login credentials represent some major security concerns.
That’s why the discovery of this database, containing 26 million sources of information, is considered a major alert.
What’s in the Database?
Coming in at a huge 1.2TB, the database – which was discovered by NordLocker – contains the following:
- 26 million login credentials
- 2 billion browser cookies
- 1.1 million email addresses
- 6.6 million various files including Word, PDF and image files
These numbers are, of course, huge. And it’s a safe bet that some serious data has been compromised along the way. It has also been revealed that the malware made a point of creating an image file by taking a screenshot via active webcams on infected devices. This, again, is troubling as it underlines the danger contained within the malware for compromising personal data.
The actual malware behind these data harvests is currently unknown. It is believed, however, that its method of attack is fairly standard. Upon infection, the malware will connect to a remote server where it can transmit any stolen data. The compromised data, as NordLocker found, was being hosted on a cloud-based hosting service and has now been taken down. But it’s likely that this database has already been traded and is out in the digital wild.

How Do You Protect Yourself?
Attacks such as this are sadly commonplace in the modern age, but there is a lot that you can do to protect your organization’s data:
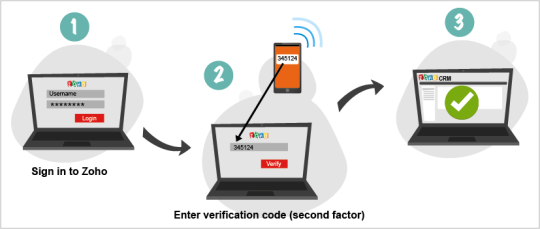
- Use Two-Factor Authentication: The combination of a username and password may seem strong, but it can be made even stronger by two-factor authentication. This additional layer of security requires the use of a unique piece of data transmitted to a device separate from your IT network.
- Install All Updates: The attack in question could easily have been caused by a vulnerability put in place by outdated technology. Both software and hardware require regular updates to patch any issues that may be discovered post-launch. And it’s your responsibility to install these as soon as possible to close any potential back door attacks.
- Regularly Monitor Network Activity: If significant amounts of data are being stolen and transmitted to a remote server, this activity will be associated with a rise in outgoing network activity. Therefore, it pays to keep a close eye on any spikes in traffic to minimize the impact of any breach.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More