The Sony data breach in late 2014 has caused embarrassment towards their own top executives and employees. Here is a timeline of the Sony hacking events.
Here’s the timeline of the 2014 Sony Pictures Cyber-attacks:
November 24

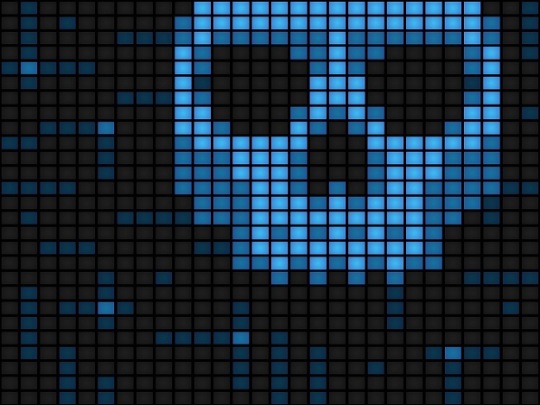
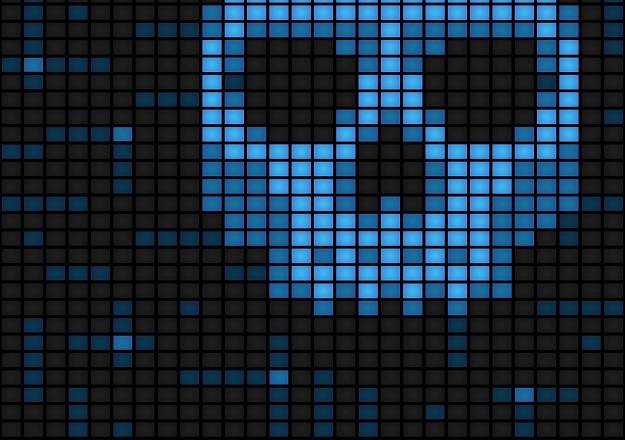
Early morning at Sony Pictures Entertainment Headquarters, based in Culver City, an image of a skull with long skeletal fingers simultaneously appeared on all employee’s computer screens. The image contained a threatening message saying, “This is just a beginning. We’ve obtained all your internal data.” This was noted to be the first sign of the digital break-in.
November 25
Computers at Sony headquarters in Culver City and overseas remain shut down. The spokesperson of Sony Pictures Entertainment said that they were investigating an IT matter. However, several news organizations report that Sony has suffered a digital security breach.
November 26
Sony employees continue working even without computers and other digital technologies, such as voicemails and emails.
November 27

Five Sony films were leaked online and made available on on-line file-sharing hubs. Four of the five films are yet to be released. Included in the films are Brad Pitt’s Fury, Annie, Still Alice, Mr. Turner, and To Write Love on her Arms.
November 28
Initial reports surface that Sony Pictures Entertainment suspects North Korea being the one responsible for the attack. Sony beleives that the attack is in retaliation for the film “The Interview”. The story is about a plot to assassinate the North Korean dictator.
November 29

Sony’s computers are still shut down.
November 30
The speculation and reports indicate that North Korea is behind the cyber-attack.
December 1
Multiple confidential Sony documents were leaked including the pre-bonus salaries of Sony’s executives. The information also includes salary details of more than 60,000 Sony employees. Executive figures are published in many sites, including Deadline. Sony works with the FBI to investigate the attack.
December 2
A company-wide alert was delivered to employees about the attack, which was issued by Sony’s chiefs Amy Pascal and Michael Lynton.
December 3
Critical information has been extracted from a big dump of stolen data which included a large list of account credentials, YouTube authentication credentials, UPS account details, all in plain text. To add to this, it also included a collection of scathing critiques of Adam Sandler movies along with files containing information on passports and visas of crew and cast members who have worked on Sony films. Some of this confidential information is published on online sites, including a 25-page list of workplace complaints of Sony employees.
Sony stated that the investigation is on-going.
December 4

A Flash warning from the FBI is made regarding the malware attack, named Destover Backdoor, and alerted all large American security departments.
Press reports also stated that some cyber-security experts found out some significant similarities between the codes used in the cyber-attack of South Korean companies and government agencies, which were also blamed on North Korea and the codes used in the Sony attack.
December 5
The Sony attackers who are claiming to be the “Guardians of Peace” sent Sony employees an e-mail threating them that they will hurt their families if they don’t sign a statement disclaiming the company.
December 7
Further data leaks occur involving the financial details from Sony Pictures. According to Bloomberg, the leak traces back to a hotel in Thailand where an executive from Sony was lodging there at the time.
North Korea praised the attack by calling it a “righteous deed” and denied any involvement in the attack.
December 8
More leaks, which were uploaded to pastebin, were added but were soon taken down. This information illustrated details of email archives belonging to two executives; the President of Sony pictures and his co-chairman, Steve Mosko. This leak was believed to have not been North Korea; it most likely came from a disgruntled employee group.
December 10

More legitimate leaks are disclosed, this time pertaining to details of tracking film piracy activities. Such activities include showing Sony’s internal anti-piracy procedures and details regarding the five ISP (Internet Service Provider) giants, used to monitor illegal downloads.
December 12
News reports from Buzzfeed, Bloomberg News, and Gawker stated that stolen documents from Sony were released, which included the medical records of Sony employees. The listed medical conditions include liver cirrhosis, cancers, and premature births.
December 13
Further genuine leaks are involve financial account information, showing revenues, expenditures, past and current projects, and deals, of which are all current still to Sony.
December 14

The latest batch of stolen Sony documents was released by the hackers. Included in these documents is the latest version of the script of “Spectre” which is the next James Bond Film. Sony hired famous litigator David Boies who sent a letter to different news organizations demanding that they erase all stolen information that the hackers had provided them.
December 15
Former employees of Sony filed a class-action lawsuit against the studio with the claim that Sony took inadequate security measures to protect their personal data.
December 16
The hackers sent an e-mail to reporters threatening to attack movie theaters that will show “The Interview”, which was set to premiere on Christmas Day. The communication sent by the cyber terrorist to the reporters even mentioned that they should remember the 11th of September 2001. They also threatened to fill the world with fear to show to the people that Sony Pictures Entertainment has created an awful film (The Interview).
Another batch of data was released including a huge number of e-mails stolen from Sony’s co-chairman and CEO Michael Lynton. Former Sony employees filed a second class-action suit with the claim that Sony was negligent in not protecting their personal data.
In connection with the threat made by the hackers to theaters, Sony told theater owners to cancel the showing of the film “The Interview” if the threats of the hackers worry them. In response to this, Carmike was the first chain to declare that it will not show the film. Landmark Theaters also said that the New York premiere of the same film was been cancelled.
December 17

Sony Pictures Entertainment pull the planned release of the film “The Interview” on Christmas Day in connection with the threat of the cyber terrorist to attack theaters that show the film. Moreover, Sony also pulls every TV advertisement of the film.
December 18
The hackers praised Sony’s decision of pulling the premiere of the film and said that as long as the film was kept out of theaters the threat will end. However, there is still a high chance of attack if the film is to be released in VOD (video on demand).
December 20
North Korea invites the United States to take part in a joint investigation regarding the Sony attack as a proclamation of their innocence. However, they warned the United States of “serious consequences” if ever they retaliate.
December 23
Sony decided to move ahead with the release of the film on Christmas day and allow it to be screened across participating theaters. Simultaneously, the film would be planned to be released in VODs. Sony claimed victory for this decision since they have never given up a film before.
December 30
Sony made the film available for rent online.
Final thought …
This timeline for Sony Pictures Entertainment Cyber Attack serves to create a better picture of what all the fuss was about. With so many events, it can be confusing to keep up with the news; therefore, we hope some value is found from understanding what such a run of malicious attacks can do to a company, even as big as Sony Pictures. Stay safe and always keep your systems and networks up to date.
For more ways to secure your data and systems, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More