The coronavirus is the latest health scare to be spreading across the globe. Hackers, as clever as ever, are using this fear to spread malware.
Hackers are innovative criminals and are constantly on the lookout for exploits. Sometimes these are software vulnerabilities that leave back door opens. But these exploits can also take the form of social engineering. And this is how hackers are taking advantage of the panic caused by the coronavirus.
It’s always important to safeguard your defenses with the best security software, but this isn’t enough. Threats such as social engineering require a concerted effort to be made by individuals. So that’s why we’re going to take a look at the threat posed by the coronavirus malware.
What is the Coronavirus Malware?
The entire planet is preparing and educating themselves for the fight against the coronavirus. Naturally, this means that millions of people are heading online to learn more about the disease. Now, although the internet poses no threat to your physical health, the same cannot be said for your digital security. And this is because cyber criminals are disguising malware as educational documents on the coronavirus.
These documents, which have been detected as docx, pdf and mp4 variants, promise to be helpful. But, rather than containing useful information on the coronavirus, these documents actually contain a wide range of malware threats. So far, Kaspersky, have identified 10 file variants that include various Trojans and worms. However, given the on-going threat of the coronavirus, it’s likely that the number of malware threats will increase.
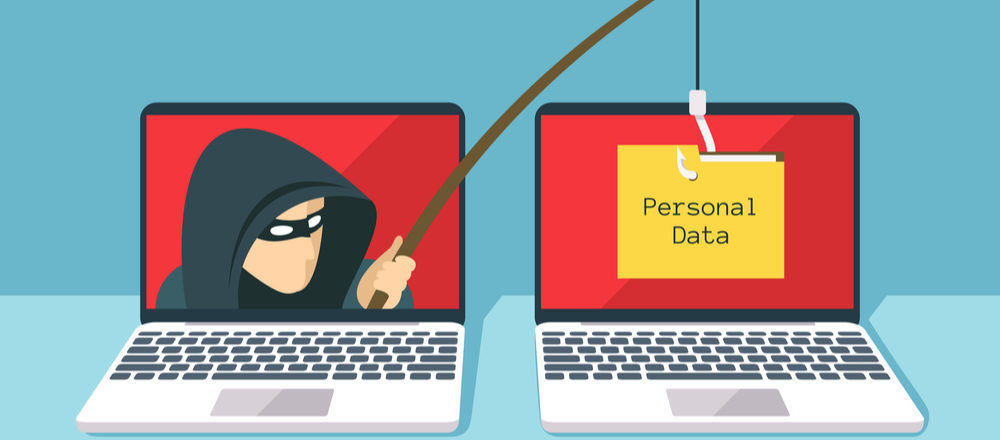
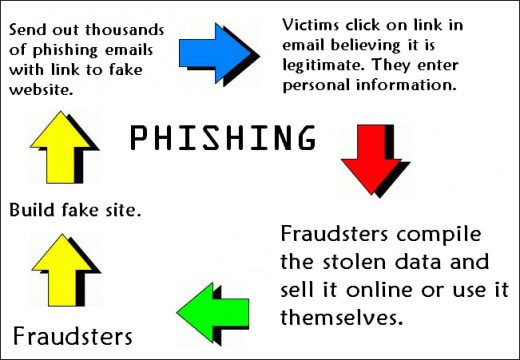
The most common method to spread this malware is through phishing emails. And, as with all social engineering, the bait is very convincing. The emails claim to be distributed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but this is a false claim. If you look a little closer you will discover that the domain these are sent from is incorrect. The official domain for the CDC is cdc.gov but these malicious emails actually originate from cdc-gov.org. These emails contain a link which, rather than taking you to an advice page, takes you to a fake web page that aims to steal your credentials.
How to Protect Yourself Against the Coronavirus Malware
Hackers are using a variety of methods to exploit the coronavirus to cause digital chaos. Infected documents threaten the security of your PC systems and phishing emails have the potential to steal personal information. Therefore, you need to protect yourself by following these best practices:
- Only Open Trusted Files: The only files that you should ever open on a PC are ones that come from a trusted source. If there’s even the smallest doubt over the legitimacy of a file you shouldn’t download it. Always check with an IT professional before going any further.
- Always Hover Over Links: Emails, and websites, can easily display a web link which disguises its true destination. A link that, for example, claims it will send you to an official government website can easily send you somewhere else. However, if you hover your mouse cursor over a link, this will prompt a popup which displays exactly where it will take you.
- Install Security Software: A sure fire way to avoid the wrath of malicious websites is by working with security software. These applications are regularly updated with details of malicious websites and will put an instant block on visiting them.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More