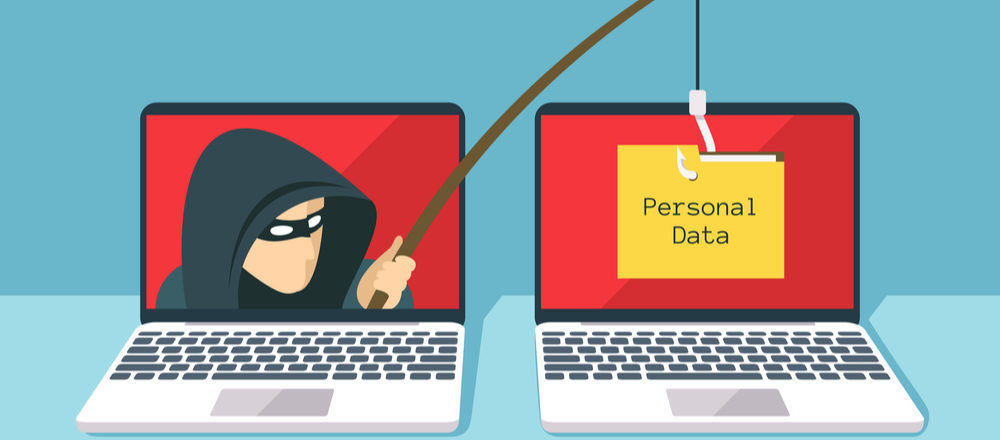
Email is an integral part of business communication for any organization with an IT structure, but there’s a significant danger posed by phishing emails.
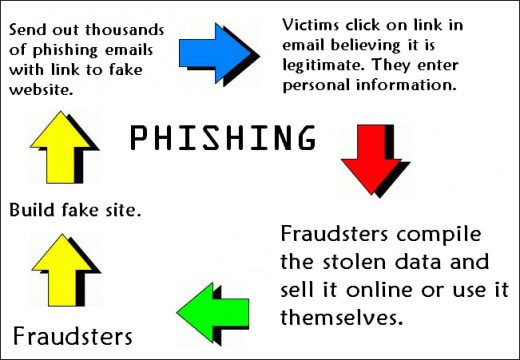
When it comes to IT security, you want to make sure your defenses are as strong as possible in order to repel any hackers. However, human error will always play a factor in this and hackers are well aware of this vulnerability. Phishing emails are the latest evolution in the age old scenario of a confidence trick and present a major issue not just to individuals and businesses, but also political parties. Given the damage that phishing emails can cause to your data security and IT infrastructure, it’s important to understand the telltale signs of a fishing email, so let’s take a look.
Four Telltale Signs of a Phishing Email
If you know what you’re dealing with then a phishing email can be quickly identified and deleted from your server within a few seconds. However, understanding what does and doesn’t make a phishing email is a learning curve. In order to get up to speed on what constitutes a phishing email make sure you look out for the following:
- A Suspicious Email Address: Although it’s possible to mask the true identity of the original sender of a phishing email, the chances are that the hacker will instead use an email address that appears to be genuine but, upon investigation, is false. A good case in point is when the email address is clearly not official e.g. it’s common to find phishing emails pretending to be from Microsoft, but with a domain name which clearly isn’t Microsoft such as microsoft_support@yahoo.com
- A Vague Greeting: Phishing emails are rarely sent to a single individual. Instead, hackers tend to send the same email to thousands upon thousands of different people. This approach ensures that there’s a higher chance of someone falling for the scam. However, addressing each email to each individual would be incredibly time consuming. Therefore, a sure sign of a phishing email is one that commences with a vague greeting such as “Dear Sir/Madam” or Dear Customer”
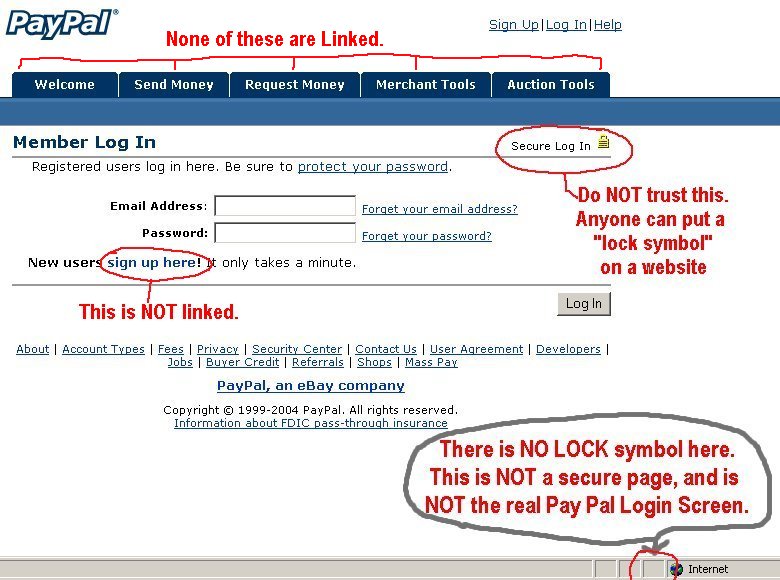
- A Fake Link: Phishing emails almost always contain a link that takes users to either an infected website or downloads malicious software. And, often, these links will appear to be genuine. So, for example, there may be a phishing email that lands in your inbox from your bank that asks you to click a link to confirm some security details. However, while that link may read as bankofamerica.com it may be hiding a different destination. The only way to verify this without clicking is by hovering your mouse cursor over the link and verifying the address revealed in the popup box.
- A Sense of Urgency: Hackers want you to click on the fake links contained within their phishing emails, so their approach tends to use fear to encourage clicking the link. Phishing emails, therefore, tend to carry some type of warning in order to trick you into thinking that it’s in your best interests to click the link. This can be as mundane as asking you to enter a survey to win a million dollars or more serious warnings such as the imminent closure of your bank account.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More