It’s essential for businesses to protect their data assets from any potential security threat. Here are tips to help your business achieve this.
The world of IT security, however, can be an intimidating landscape and many business owners struggle to put a plan of action together. And this leaves them vulnerable to security attacks.
Thankfully, though, we’ve learned a thing or ten about protecting data from rogue elements and will be sharing these security best practices with you.
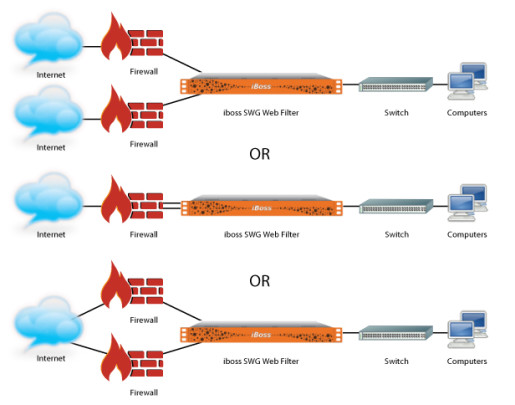
One of the best strategies to minimize data loss is by segmenting your networks. The use of firewalls between each network segment will prevent attackers gaining access to all of your data at once. It’s likely that this frustration will lead to attackers giving up and heading elsewhere.
- Visualize What You’re Securing
Data, in its purest form as binary code, isn’t something you can physically see. And it’s this lack of physical mass which means it’s difficult to assess the knock on effect of implementing new security policies. To prevent leaving your business open for attacks, keep detailed visibility records of your networks and their configurations. This allows you to make future changes which won’t compromise your security.
There needs to be a level of control when it comes to your network, so you can’t issue everyone admin rights. Sure, it may save users a little time in sorting out network issues such as installing new hardware, but it also sets your network up for an attack by making admin rights less privileged.
- Keep Tabs
It’s vital that you create a ‘security knowledge’ database to help keep everyone on the same page as to who has specific access to which security features. This allows a hierarchy to be observed and easy to understand processes to be carried out when dealing with applications or even decommissioning them.
- Carry out Security Training
Everyone in your organization will need to undergo some form of security training. This allows your business, as a whole, to be more secure from attacks. And it doesn’t need to be intense training either, it may be as simple as going through the company IT policy with new starters or regular email updates about current viruses and malware.
The easiest security attack is one that targets a known vulnerability e.g. an opportunity to get into your system via a ‘back door’ in a piece of software. Therefore, always make sure you install every patch you’re offered as it could make a huge difference to your chances of staying secure.
- Analyze your Security Stats
The only way to confirm that your security efforts are working is to analyze their performance every month. This is why you will want to measure metrics such as number of attacks, user errors etc. to monitor exactly which direction your security is heading in.
Communication needs to be clear and defined between your security team and other in-house teams to guarantee high levels of security. Any changes that are made in-house need to be communicated between security and the corresponding team to allow security provisions to be updated/implemented. Likewise, your security team has to inform all other teams of any upcoming security changes to keep everyone aware.
- Reduce Outbound Access
Many data thefts occur from within businesses, so it’s good practice to limit the amount of outbound access available. So, if, for example, your business has no need to use Google Docs then put a block on it and prevent any data leaking out via this avenue. Don’t forget: insider data theft can not only be disastrous, but also highly embarrassing.
- Automate Certain Security Tasks
It’s a tough job to monitor every single aspect of your data security, so why not automate some of the more basic tasks e.g. monitoring unauthorized attempts at bypassing firewalls. This gives your security team more time to concentrate on more complex security issues.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More