Forgetting a password is frustrating, so the promise of a password recovery tool is tempting. Until, that is, you find out it’s packed full of malware.
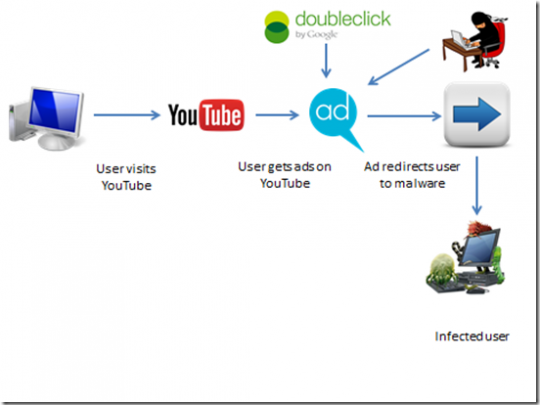
If something online sounds too good to be true, then it usually is – see the numerous adverts on YouTube which promise to make you $50k a month with minimal effort. And this is exactly the case with the Sality malware. Naturally, Sality doesn’t advertise itself as malware. Instead, it bundles itself stealthily, as a hidden extra, alongside a password recovery tool for Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) and Industrial Control Systems (ICS). Whilst the tool does indeed help you to extract passwords, the presence of Sality opens a whole world of digital pain.
The Lowdown on Sality
Sality, in its earliest form, is believed to have been online for nearly 20 years, so it’s certainly not a new threat. However, over the years, its evolution has led to its modern variant becoming a nasty piece of malware. At present, it’s making its way into people’s PCs thanks to relatively crude, yet tempting adverts on social media sites. Advertising itself as a free download, the tool will retrieve passwords for PLC and ICS – through a vulnerability in the system’s firmware – but it also activates the Sality malware.
To understand how Sality operates, you first need to know what a peer-to-peer (P2P) botnet is. Used to generate huge amounts of processing power – usually for cracking passwords or mining cryptocurrency – a P2P botnet obtains this power by hijacking large numbers of PCs. These hijacked PCs are then forced to work together on the same task – after all, 1,000 PCs mining cryptocurrency are going to achieve their objective a lot quicker than a single PC. It appears that Sality is currently focused on cryptocurrency, but there is nothing to stop threat actors unleashing more powerful attacks e.g. taking entire IT systems down.
How Do You Handle a Sality Infection?
While Sality may have been around for some time, it hasn’t learned every trick in the book. For example, not only will it throttle an infected PCs performance by using 100% of its CPU, it also triggers numerous Windows Defender alerts. However, it does have enough sense to scan any PC it lands on for anti-virus software before shutting down any identified tools. Therefore, it’s crucial that you follow preventative approaches to avoid Sality:
- Do Not Trust Online Adverts: legitimate password recovery tools are unlikely to be advertised on social media sites. If you have forgotten your password, then you should contact the software developers for advice. Alternatively, you can create secure backups of your passwords with an app such as Google’s Password Manager.
- Remove Download Privileges: almost every malware threat involves a malicious download and, as such, it makes sense for your organization to limit the number of downloads taking place. By limiting download privileges to, for example, line managers, you will minimize the chances of malware being downloaded by mistake.
- Block Social Media: if you want to make sure that you are specifically limiting the risk of Sality, you can simply block access to social media sites from within your organization’s network. However, be aware that Sality is likely to be lurking elsewhere on the internet.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More