If you use Internet Explorer as your web browser, pay close attention to a recent Zero-Day vulnerability CVE-2014-8967 found allowing remote code execution.
Out of the various web browsers available to download, Internet Explorer is often the most vulnerable for attacks since it happens to be the one that is widely used globally.
We will summarize here what you need to know about CVE-2014-8967.
What is a Zero-Day vulnerability?
Microsoft and anti-virus companies regularly release updates and new virus definitions to address these exploits. Zero-day means the exploit or bug is so new that no company has had a chance to patch it yet.
Specifically for zero-day vulnerability CVE-2014-8967, Internet Explorer has been exploited by hackers who have piggybacked on its publicly accessible framework to execute arbitrary code.
- Technically speaking, the Internet Explorer vulnerability is all about the way in which it references “counting”, to allocate given in-memory objects.
- These in-memory objects represent elements pertaining to HTML, otherwise known as CElement Objects.
- An additional CSS style is applied, which illustrates the style it displays.
- This change creates a loophole in the browser where the object’s reference can be allowed to drop down to zero before it normally should.
- This in turns causes the object to become available to accept other commands to run.
- This is where an opportunist can exploit the vulnerability to run code within the given framework.
- The danger lies in the privileges the attacker can have on your system.
- For instance, if you have administrator rights, the hacker can also acquire this same right, that’s if they manage to successful carry out the browser vulnerability hack.
- It’s not much of a high risk if your account has basic user rights. Regardless of the level of user permissions you have, such an attack is undesirable.
Examples
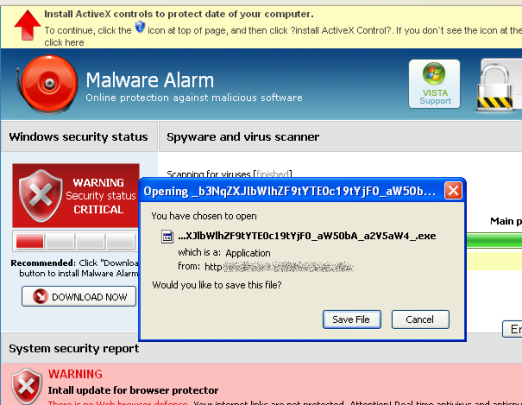
An example of such an attack can originate via a dodgy website such as a hosted site managed by the attacker, is configured to apply the Internet Explorer vulnerability.
All that is needed is some sort of user action, such as a prompt, to trick the user into visiting the malicious site.
Another way hackers can use this vulnerability is by targeting other compromised websites to do the same thing.
Regardless of the malicious intent, you’re always in control and should practice safe browsing by avoiding suspicious or unfamiliar websites.
It can all begin by accidentally by opening an infected file or unknowingly visiting a malicious web page, which executes the browser vulnerability.
This is why we stress the importance of not opening unknown recipient messages that contain attachments or links within emails and other places such as web banners or message boxes. The best thing to do is close down the page or delete those suspicious emails and notify your IT administrator.
Prevention and protection
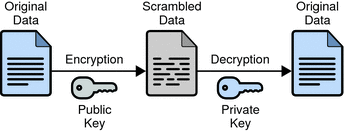
The good thing about all the Microsoft mail clients, such as Microsoft Outlook Express, Microsoft Outlook and Windows Mail, is that they all disabled Active X and scripts by default. This stops malicious code from launching itself automatically and creating a problem, as discussed previously. However, you still need to be careful not to open unknown files or links.
How to protect yourself from Zero Day Internet browser vulnerability:
- Update your Operating System. Do this with Windows Updates and be sure to apply any critical patches.
- Do not Open attachments. It can all begin by accidentally opening an infected file or a malicious web page to execute the browser vulnerability. This is why we stress the importance of not opening unknown recipient messages that contain attachments or links such as web banners.
- Use a different browser. Using a different browser can prevent the typical browser exploits found on Internet Explorer. For example Chrome, which is one of our preferred web browsers to use.
- A little configuration can go a long way. Within Internet Explorer settings, you can set the option to prompt before allowing “Active scripting” to run, or alternatively, disable “Active scripting” within “Internet and Local intranet security zone settings”.
- Use EMET. This is more for system administrators; however EMET (an Enhanced Mitigation Experience Tool Kit) can prove invaluable. This will be necessary I’d you’re working in a company that is unwilling to move away from Internet Explorer. EMET is a great workaround to help you to avoid this vulnerability.
For more ways to pro-actively protect your business and data from malicious vulnerabilities, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More