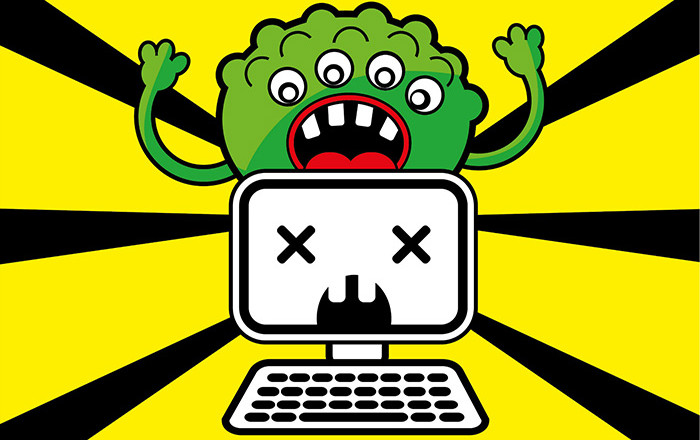

Some websites are seen as trusted, but malvertising is a new threat to the world of cyber security and may cause every website to be viewed with caution.
Now, we’ve all been irritated by online ads whilst trying to enjoy our favorite websites, but, with the advent of malvertising – short for malicious advertising – they’ve reached a new level of irritability. And it’s a threat that has the potential to affect everyone with popular sites such as Spotify and Reuters already falling victim.
As it’s such a new threat, it’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the signs and symptoms of malvertising in order to protect your data and feel safe.
What is Malvertising?

Popular websites tend not to handpick their adverts and, instead, they turn to third party ad networks who are able to use complex algorithms and read cookies (tracking files left legitimately by websites) to deliver bespoke adverts to visitors.
And, what many people are unaware of, is that when you connect to sites such as Spotify and Reuters, you’re also connecting to a number of other web addresses and these can include third party ad networks. Naturally, this instantly provides a number of routes for hackers to exploit that the web user is completely unaware of.
With malvertising, hackers use these footholds to deliver malicious adverts which may appear to be genuine, but contain malware. Sometimes the web user will need to click on the ad to activate its payload, but many other forms of malvertising will embed scripts in the affected webpage to automate the execution and infect the user.
Malvertising is also particularly effective as it’s able to ascertain details of the user’s operating system and web browser which is crucial for hackers to launch specific attacks e.g. Firefox running on Windows XP will have different vulnerabilities to Internet Explorer running on Windows 8.
Hackers can also target specific individuals by infecting ads which use specific keywords e.g. a lawyer looking for “lawyer briefcase”, so this, again, highlights just how sophisticated and bespoke a method of hacking malvertising is.
Combatting Malvertising

Malvertising may be new, but it doesn’t mean you need to panic about being defenseless. In fact, if you follow the advice below then you should find you’re well protected from malvertising:
- Keep your browsers updated – Internet browsers such as Chrome and Internet Explorer are designed with safety measures in place to identify websites exploited by malvertising. However, you need to ensure that your browser is up to date to ensure you’re protected from the latest threats.
- Update Flash – We’ve discussed the security flaws in Abobe Flash before and it’s no surprise to discover that malvertising just loves to exploit Flash. Therefore, it’s crucial that all patches and updates are installed as soon as possible. Or, alternatively, just disable Flash from running at all times.
- Use ad-blockers – Popular with many users, ad-blockers prevent ads from being displayed and prevent users clicking on them and activating malware. These may, however, block genuine adverts that are necessary, but these can easily be put on ‘exceptions’ lists.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More















 It’s common to assume that all security threats originate from outside your organisation, but the truth is that sometimes
It’s common to assume that all security threats originate from outside your organisation, but the truth is that sometimes  Windows 10 has certainly come in for criticism
Windows 10 has certainly come in for criticism