A hacked network is a disaster for any organization, so keeping things secure is vital. However, sometimes things go wrong and you need to know what to do.
Your IT operations are supported by your IT network, so, if it gets hacked, there’s every chance that all those PCs you have lined up in your offices will be unable to operate. Naturally, this means that productivity will drop off almost immediately and affect not just you, but also your customers. With good IT practices in place, you significantly reduce the risk of this happening. Mistakes, be they caused by hardware or human error, are inevitable, though, and it’s rare that a business can claim to have defenses which are 100% secure.
Therefore, it’s important that you know what to do when your network is hacked. Rather than have you learn the hard way, through experience, we’re going to save you some of the pain with a quick guide on how to cope.
Steps to Take When You’re Hacked
Most importantly, you need to take the following steps when you discover your network has been hacked:
- Put Everything On Lock Down: The stealthy nature of hackers means that it’s difficult and time consuming to determine exactly how much of your network the hackers have breached. So, in order to preserve as much as your network as possible, you have to assume the worst: they’ve gained access to everything. And that’s why you need to lock down and change passwords on everything be it folders on a shared drive or your social media accounts. This is the only way to minimize damage.
- Run an Anti-Virus: Following a network breach, the next step taken by hackers is most commonly one that involves downloading and executing malware. This can range from helping to set up DDoS attacks, installing keylogger software to facilitate data theft or even executing ransomware attacks. It makes sense, therefore, to run your anti-virus software as a priority to prevent the network attack escalating further.
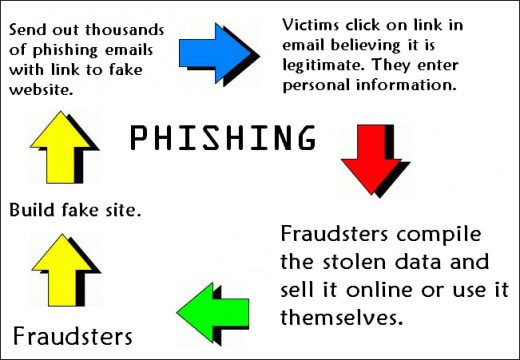
- Understand What Allowed the Hack: Understanding the source of the hack is essential in understanding what has been compromised and also nullifying the security threat. So, for example, if you’re able to pinpoint the network breach to an infected email that was received, then it’s likely that everyone in the address book of that hacked account is at risk. Immediate action such as contacting those at risk can then be taken to help prevent the hack spreading further.
- Learn from the Experience: As we’ve stated, it’s likely that your network will, at some point, experience a security disaster. However, while in the short term this may feel like nothing but non-stop chaos, there’s an important set of learning to be absorbed for the long term. Mistakes are what allow us to evolve and make better decisions in the future, so make sure you take the opportunity to analyze exactly what went wrong and the steps you can take to prevent it happening again.
Final Thoughts
A hacked network represents every IT professional’s worst nightmare, but it’s important that you understand the best steps to take in this situation. Not only does it prevent network hacks from escalating into more devastating hacks, but there’s also the chance to learn and strengthen for the next time hacker aims an attack at your network.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More