Local backups are one of the most popular forms of backing up data, so it’s a method that organizations should seriously consider for storing their data.
While cloud backups are grabbing all the headlines, they’re not necessarily the definitive answer to everyone’s backup needs. What’s more, local backup can easily run alongside cloud backup systems, so they’re not an option which should be dismissed.
As backup is such a critical business need in an era of huge data growth and ransomware threats, we’re going to take a look at what local backups are and what they can do for your business.
What is Local Backup?
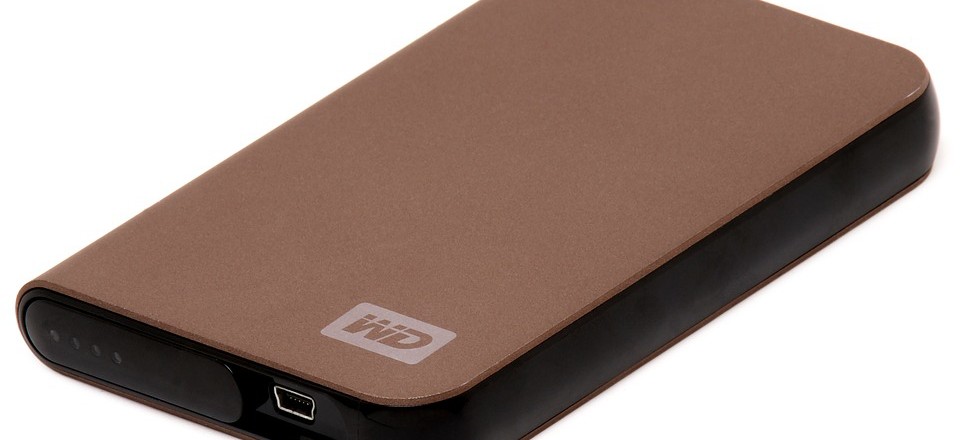
As the name suggests, local backup is any type of physical storage medium which is kept locally and can be quickly connected to a PC/network which requires a backup to be saved or restored. The most popular forms of local backup are:
- External Hard Drives – These devices are now capable of holding huge amounts of data with 16TB (that’s 16,000GB) external hard drives available. Usually connected through USB ports, these hard drives provide a swift transfer of data and this is even quicker when USB 3.0 capabilities are present.
- CDs, DVDs and Blu-Rays – Optical drives may sound fairly limited in their storage capacities (a single layer Blu-Ray holds 50GB and a CD only 750MB), but they’re still highly popular for quick data storage that can be kept close at hand on a spindle.
- Solid State Drives – USB and flash drives, again, are highly quick and simple methods for storing critical data which can be kept locally. The beauty of this small, but important method of backup is that implementing the backup data is easily achieved by simply plugging the medium into the PC.
What Can Local Backup Do for You?
Local backup solutions come with a number of benefits which mean they’re perfect for organizations and these can include:
- Enhanced Security – External hard drives, optical drives and solid state drives are all protected by online threats such as hacking as they’re standalone pieces of kit. Once they’re disconnected from a PC or network there’s no way of them being hacked, so they represent a highly secure storage medium for your data.
- You Have Full Control – One of the main drawbacks of cloud backups is that they tend to be operated by a third party contractor, so you never truly have full control and responsibility for your data. With local backup methods, however, your data is always safely under your own watch and does not leave your premises.
- Quicker Transfer – Local backups have a much simpler structure than complex cloud backup systems, so your data can be transferred at a much quicker rate when necessary. This reduces downtime for your PC and network whilst also significantly reduces the time taken to monitor the backup process.
As a result, local backups represent a secure method of storing data with a number of benefits that cloud backups are unable to offer. However, many organizations are now embracing hybrid systems which utilize local and cloud backups to enhance the ability to retrieve data when it’s needed most.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More