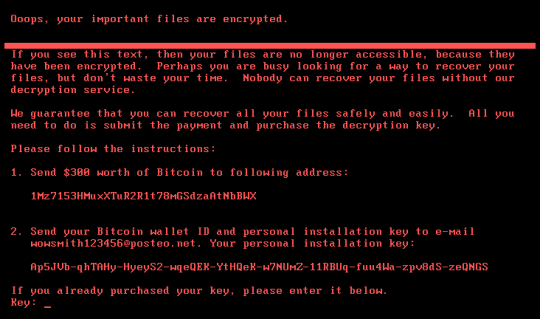
A major cyber attack has swept across the globe and, once again, it’s taken the form of ransomware to shut down computers and demand Bitcoin ransoms.
Known as Petya – the Russian word for stone – has managed to halt operations at a chocolate factory in Australia and even one of Russia’s biggest oil companies, so the scale and sophistication of its attack is clear to see. Following the recent WannaCry ransomware attack, Petya has made headlines in a security landscape where safety appears to be far from guaranteed.
As this is such a widespread attack – and the fact that new ransomware attacks are appearing weekly – it seems like the perfect time to look at Petya and reinforce what you can do to protect yourself.
The Story behind Petya
Although it’s difficult to confirm, it’s believed that the Petya attack originated in the Ukraine. Reports suggest that the ransomware was spread through the update server for MeDoc which is a popular brand of Ukrainian accounting software. Consumers believed they were simply downloading a new update for their software, but it was actually a powerful slice of malware which then spread like wildfire.
This latest variant of Petya, however, is even more powerful than its original incarnation. It’s believed that Petya now comes loaded with a tool named LSADump which harvests data and passwords from all the PCs located on that network. Petya also appears to be encrypting every single file on the infected PCs through the master boot record – this helps your PC boot up Windows at startup.
Most disturbingly, though, it’s being reported that Petya may not even be ransomware and may, instead, simply wipe everything from a PC with no chance of recovery. While the thought of having to pay a small ransom to retrieve data is troubling enough, the idea that your data may never be retrieved brings a whole new level of concern to Petya.
Defending Against Petya
Regardless of whether Petya encrypts or destroys files, it remains a highly sophisticated strain of malware that no PC user wants to find on their system. Kaspersky and Symantec have assured consumers that their anti-virus software will actively identify and protect against Petya, but for many users this may be too late.
Unfortunately, despite the spate of attacks taking advantage of Windows vulnerabilities, many PC users are still incredibly lax when it comes to installing security updates and patches. The main reason for this procrastination is an issue of time, but what’s five to ten minutes of installing updates and rebooting compared to having all the files on your entire network encrypted or even deleted?
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More